Cervical Cancer, Uterine Cancer and Bartholin’s Cyst have been in the news. Cervical Cancer is not the same as Uterine Cancer. Bartholin’s Cyst is also different from both of these gynecologic cancers.
Cervical Cancer
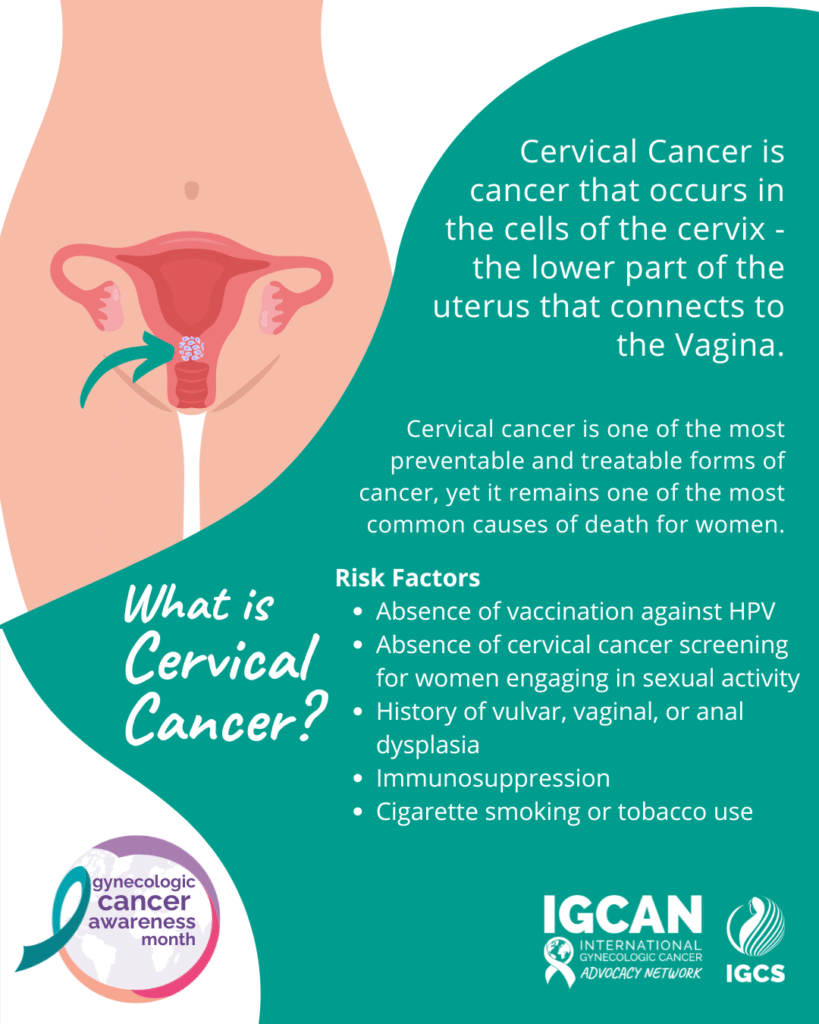
Depending on the Source (DotS) the definition of cervical cancer may vary. In About Cervical Cancer the International Gynecological Cancer Society’s (IGCS) definition is:
Cervical Cancer Signs and Symptoms
What are cervical cancer common signs and symptoms?
In Cervical Cancer: Signs and Symptoms the IGCS explain:
- Irregular blood spotting or light bleeding between periods in women of reproductive age
- Postmenopausal spotting or bleeding
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse
- Increased vaginal discharge, sometimes foul smelling
Many women wait too long to seek medical help or may not have easy access to care. As cervical cancer advances, more severe symptoms may appear including:
- Persistent back, leg or pelvic pain
- Weight loss, fatigue, loss of appetite
- Foul-smell discharge and vaginal discomfort
- Swelling of a leg or both lower extremities”.
Uterine Cancer
DotS the definition of uterine cancer may vary. In Uterine Cancer: Types of Uterine Cancer the IGCS’s definition is:
Uterine Cancer Signs and Symptoms
What are uterine cancer common signs and symptoms?
In Uterine Cancer: Signs and Symptoms the IGCS explain:
- Vaginal bleeding after menopause
- Bleeding between periods
- An abnormal watery or blood-tinged vaginal discharge
- Pelvic pain or pressure”.
Bartholin’s Cyst
What is a Bartholin’s Cyst?
DotS the definition of a Bartholin’s Cyst may vary. In Bartholin’s Cyst [+ Image] the (United Kingdom) NHS’s definition is:
Bartholin’s cysts usually affect women aged between 20 and 50 years. They can affect anyone with a vagina”.
Where may I find an image of at a Bartholin’s Cyst?
You may find an image of a Bartholin’s Cyst in the (United States) Mayo Clinic’s Bartholin’s Cyst.
Tracking
Tracking or keeping a record of your menstrual periods and any unusual vaginal bleeding, pain and other symptoms can help you your health care provider work out what’s what and what’s not.
Health Care Provider
Is vaginal bleeding, other than your periods, normal?
No. It is important to get any vaginal bleeding, spotting or other symptoms that are not normal for you checked by your health care provider as soon as possible.
It can also be in your best interest not to assume that any symptoms you have are normal menopause symptoms.
Health Topics A-Z
Where may I find Health Topics A-Z related to Cervical Cancer, Uterine Cancer and Bartholin’s Cyst?
In Health Topics A-Z you may find:
Links
Where may I find Links related to Cervical Cancer, Uterine Cancer and Bartholin’s Cyst?
Your Country may have Links similar to:
Links
This Links List to third party websites is neither comprehensive nor exhaustive. Inclusion on this Links List does not imply endorsement or recommendation. Non-inclusion on this Links List does not imply non-endorsement or non-recommendation. Third party websites are not under the control of Meno Martha International Menopause Directory. Third party websites may contain explicit medical images and/or sexual references. Please read Meno Martha International Menopause Directory’s Links Policy before proceeding to a Link. Please contact Webmaster if you experience a problem with a Link.New or Updated
- Bartholin’s Cyst [23 April 2025]
- Cervical Cancer Prevention Week [19-25 January 2026, United Kingdom]
- Consumer Video and Podcast Series: 2025 Consumer Videos and Podcasts – Abnormal Uterine Bleeding—When To See A Clinician
- Endometrial Cancer [14 February 2025]
- January Is Cervical Health Awareness Month [United States]

- Update on Surgical Menopause [01 November 2025]
- Bartholin’s Cyst
- Bartholin’s Cyst [+ Image]
- Cervical Cancer
- Cervical Cancer
- Cervical Cancer Prevention Week [19-25 January 2026, United Kingdom]
- Consumer Video and Podcast Series: 2025 Consumer Videos and Podcasts – Abnormal Uterine Bleeding—When To See A Clinician
- Colposcopy
- Endometrial Cancer
- Eveappeal.org.uk
- Foundation for Women’s Cancer [United States]
- Gynecologic Anatomy
- Gynecologic Cancer Awareness
- Gynecologic Cancers
- Medically Induced Menopause
- International Gynecologic Cancer Advocacy Network
- International Gynecologic Society
- January Is Cervical Health Awareness Month [United States]

- National Cervical Cancer Coalition

- Ovarian Cancer

- Postmenopausal Bleeding
- Resources To Share: Videos – Under the Paper Gown Comedy Web Series
- The American Cancer Society Guideline for Cervical Cancer Screening [04 December 2025]
- Tips for Tracking Your Bleeding
- Types [Gynecologic Cancer]
- Uterine Cancer

- Uterine/Endometrial Cancer/GDT
- Videos and Podcasts: Interviews and Podcasts – Interviews: How Do I Deal With the Menopause After A Diagnosis of Gynaecological Cancer
- Womb (Uterus) Cancer
- Womb Cancer
- World GO Day [World Gynecologic Oncology Day, 20 September 2025]








