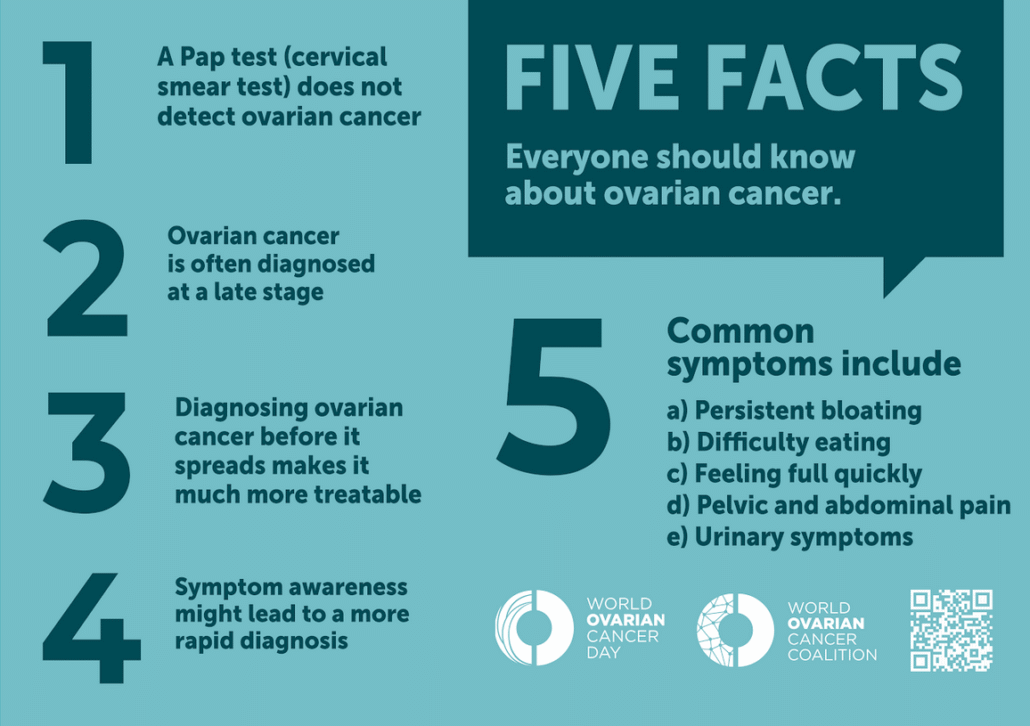
“Currently, there is no routine, simple screening test to accurately detect ovarian cancer. Contrary to popular belief, cervical screening (i.e.: Pap smear) will not detect…”.1
Umbrella
What may the Ovarian Cancer Umbrella include?
Depending on the Source (DotS) this Umbrella may include:
- Cancer of the Ovary
- Ovarian Cancer
Cancer
What is cancer?
DotS the definition of cancer may vary. The (United States) National Cancer Institute’s (NCI) definition is:
“Cancer
A term for diseases in which abnormal cells divide without control and can invade nearby tissues. Cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body through the blood and lymph systems”.2
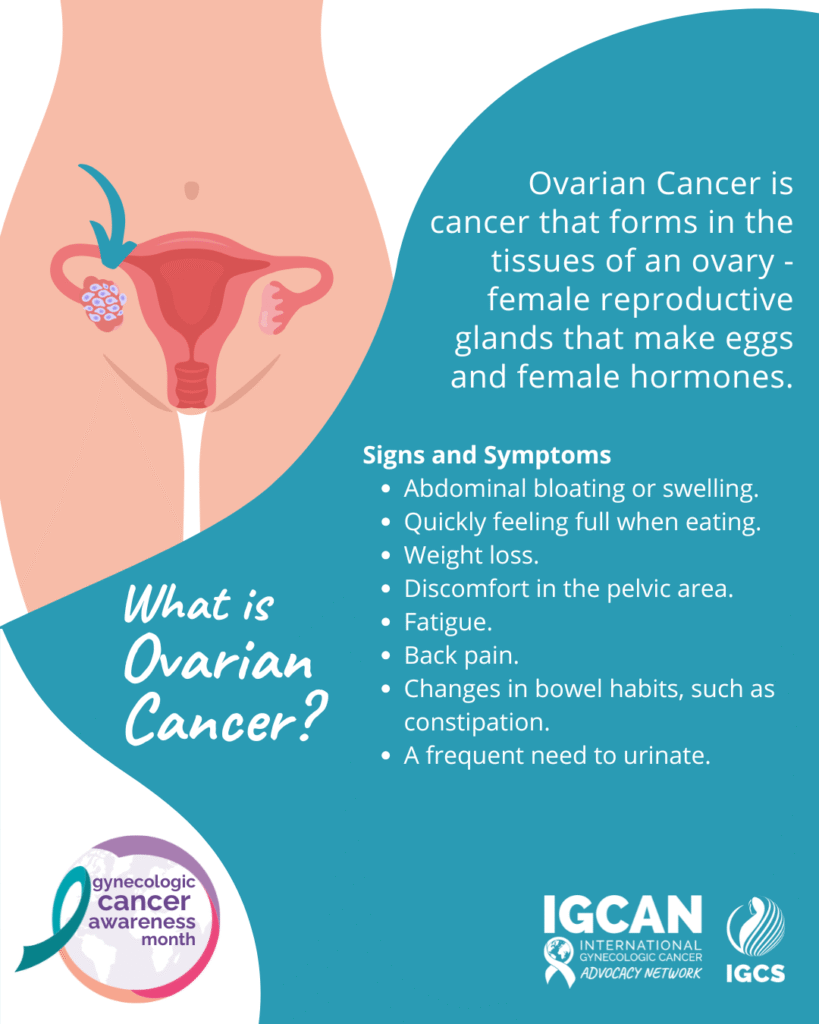
Ovarian Cancer
What is ovarian cancer?
DotS the definition of ovarian cancer may vary. The (United States) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s definition is:
“Ovarian cancer is a group of diseases that originates in the ovaries, or in the related areas of the fallopian tubes and the peritoneum”.3
Symptoms
What are the common symptoms of ovarian cancer?
In Ovarian Cancer Symptoms & Risks: What Are the Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer? the World Ovarian Cancer Coalition (WOCC) elaborate on:
Other Symptoms
What can be other symptoms of ovarian cancer?
In Ovarian Cancer Symptoms & Risks: What Are the Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer? the WOCC:
- Changes in bowel habits
- Abnormal bleeding – Any post-menopausal bleeding should always be checked by your primary health care provider or doctor
- Extreme fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss”.5
In Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer: What Are the Symptoms? the (United Kingdom) Target Ovarian Cancer also note:
- New – they’re not normal for you
- Frequent – they usually happen more than 12 times a month
- Persistent – they don’t go away”.6
Cause
What may cause ovarian cancer?
In Ovarian Cancer: Main Causes of Ovarian Cancer the (United Kingdom) NHS explain:
You may have a higher chance of getting ovarian cancer if you:
- Inherited a faulty gene, such as the BRCA genes or those linked to Lynch syndrome
- Had breast cancer or bowel cancer
- Had radiotherapy treatment for a previous cancer
- Have endometriosis or diabetes
- Started your periods at a young age or went through the menopause late (over 55), or have not had a baby – because these things may mean you’ve released more eggs (ovulated more)
- Have never used any hormonal contraception, such as the pill or an implant
- Are taking hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
- Are overweight
- Smoke”.7
Age
Is there an association between the risk of developing ovarian cancer and getting older?
In Ovarian Cancer Symptoms & Risks: What Are the Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer? the World Ovarian Cancer Coalition explain:
Your risk increase as you get older. Ovarian Cancer is more common in those aged 50-79. However, you can develop it when you are younger”.8
Common or Not
How common is ovarian cancer?
In the United States, the NCI in Ovarian, Fallopian Tube, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer Screening (PDQ®)–Patient Version: General Information About Ovarian, Fallopian Tube, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer – In the United States, ovarian cancer is the sixth-leading cause of death from cancer in women elaborate on:
In the United Kingdom (UK) Cancer Research UK note:
Pap Test
Does the Pap test check for ovarian cancer?
No. In Ovarian Cancer Testing & Detection the World Ovarian Cancer Coalition note:

Symptom Diary
Where may I find an ovarian cancer symptom diary?
Your Country may have Links similar to:
Ovarian Cancer Symptom Diary
- How To Talk To Your GP About Your Concerns: Keep Track of Your Symptoms – Ovarian Cancer Action Symptoms Diary
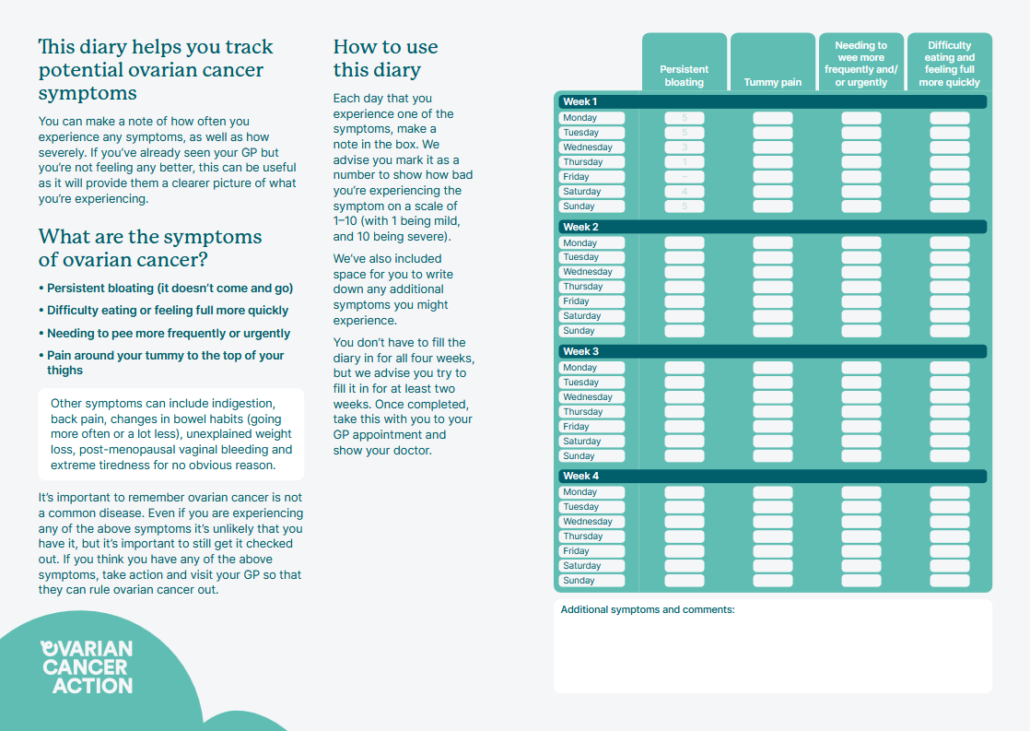
- Ovarian Cancer Symptoms: Additional Signs and Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer – Symptom Diary
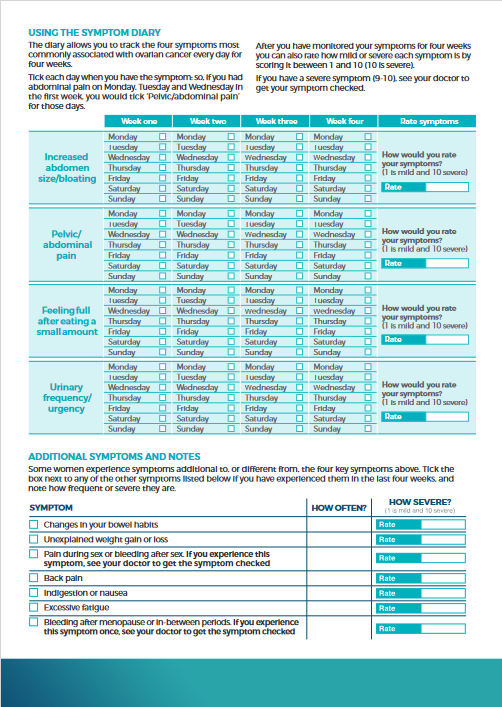
- Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer: More Support – Symptoms Diary

- Symptoms: Symptom Diary
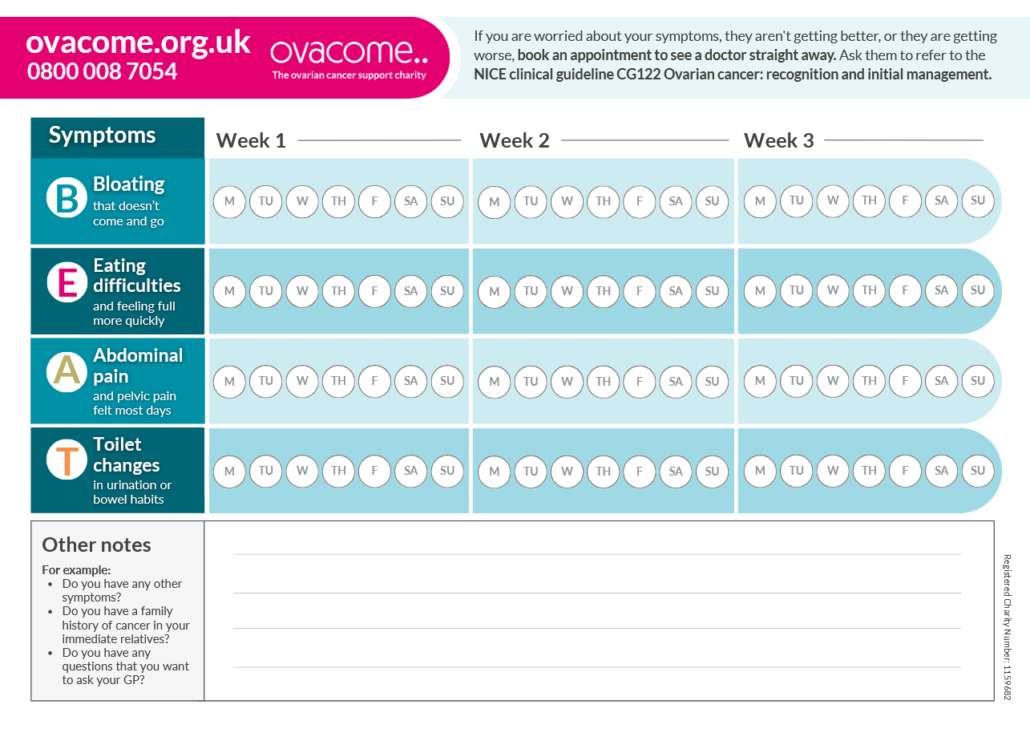
- What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer? Ovarian Cancer Symptom Diary
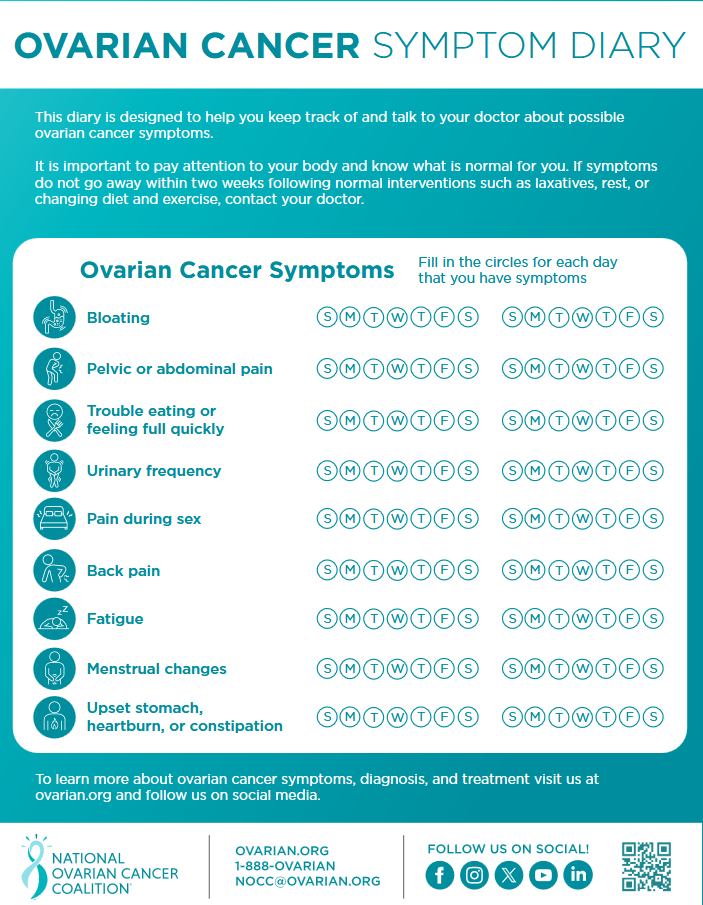
Health Care Provider
What if I am worried about some symptoms I am experiencing?
In Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer: Worried About Your Symptom? Target Ovarian Cancer elaborate on:
Tell your GP if one or more relative in your close family has had cancer especially if the cancer affected your mother, father, brother or sister. This is because ovarian cancer can run in families”.12
Who is a GP?
DotS and DotC (Depending on the Country) a GP may be a qualified and registered general practitioner, a medical practitioner, a medical doctor or a doctor.
Health Topics A-Z
Where may I find Health Topics A-Z related to Ovarian Cancer?
In Health Topics A-Z you may find:
Links
Where may I find Links related to Ovarian Cancer?
Your Country may have Links similar to:
Links
This Links List to third party websites is neither comprehensive nor exhaustive. Inclusion on this Links List does not imply endorsement or recommendation. Non-inclusion on this Links List does not imply non-endorsement or non-recommendation. Third party websites are not under the control of Meno Martha International Menopause Directory. Third party websites may contain explicit medical images and/or sexual references. Please read Meno Martha International Menopause Directory’s Links Policy before proceeding to a Link. Please contact Webmaster if you experience a problem with a Link.New or Updated
- 5 Warning Signs and Risk Factors of Ovarian Cancer
- A To Z of Ovarian Cancer

- About Ovarian Cancer
- About Ovarian Cancer

- BRCA & Lynch Syndrome FAQs
- BRCA Gene Mutations: Cancer Risk and Genetic Testing
- BRCA Gene Test for Breast and Ovarian Cancer Risk
- BRCA Genetic Test
- British Gynaecological Cancer Society (BGCS) Ovarian, Tubal and Primary Peritoneal Cancer Guidelines: Recommendations for Practice Update 2024 [September 2024]
- British Gynaecological Cancer Society and British Menopause Society Guidelines Management of Menopausal Symptoms Following Treatment of Gynaecological Cancer [August 2024]
- CA125 Blood Test
- Consumer Video and Podcast Series: 2025 Consumer Videos and Podcasts – Abnormal Uterine Bleeding—When To See A Clinician
- Eveappeal.org.uk [Eve Appeal, United Kingdom]
- Experiencing Ovarian Cancer Symptoms
- Family Health History
- February Is Ovarian Cancer Awareness Month [Australia]

- Five Facts of Ovarian Cancer
- Foundationforwomenscancer.org [Foundation for Women’s Cancer, United States]
- Genetics: What Does This Mean for Me and My Family?
- Gynae Cancer Awareness Month [September, United Kingdom]
- Gynecologic Cancer Awareness Month

- Gynecologic Cancer Awareness Month [September, United States]

- Gynecologic Cancers
- Gynecologic Cancers
- Heredity Breast and Ovarian Cancer: Family Health History and Breast and Ovarian Cancers
- Heredity Cancer and Risk
- Hereditary Ovarian Cancer

- How To Talk To Your GP About Your Concerns: Keep Track of Your Symptoms – Ovarian Cancer Action Symptoms Diary
- Lynch Syndrome [+ Video: What Is Lynch Syndrome]
- Lynch Syndrome: Everything You Need To Know
- Mayo Clinic Minute: Tips From A Gynecological Surgeon on Recovery From Surgery [+ Video Courtesy: Mayo Clinic News Network]
- Mayo Clinic Q&A: Get the Facts on Ovarian Cancer
- National Ovarian Cancer Awareness Month [September 2025, United States]

- National Ovarian Cancer Coalition [United States]
- Ovacome.. Ovarian Cancer [United Kingdom]
- Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer Action [United Kingdom]
- Ovarian Cancer Australia
- Ovarian Cancer Awareness Month [March, United Kingdom]

- Ovarian Cancer Awareness Month [September, United States]
- Ovarian Cancer Research Alliance [United States]
- Ovarian Cancer Symptoms
- Ovarian Cancer Symptoms
- Ovarian Cancer Symptoms & Risks – What Are the Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer?

- Ovarian Cancer Symptoms: Additional Signs and Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer – Symptom Diary
- Ovarian Cancer Testing & Detection

- Ovarian Cancer/Primary Peritoneal
- Ovarian Cancer: Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging – Tests for Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer: Essential Facts You Need To Know – Mayo Clinic Health System [Video]
- Ovarian Cancer: Moving To A Personalized Treatment Approach
- Ovarian Cancer: Ovarian Cancer Basics
- Ovarian Cancer: Ovarian Cancer Risk Factors
- Ovarian Cancer: Reducing Risk for Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer: Screening for Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer: Still Possible After Hysterectomy?
- Ovarian Cancer: Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian Cancer: What Is Ovarian Cancer? The Ovaries and Reproductive System: Cancers of the Female Reproductive System [+ Video]
- Ovarian, Fallopian Tube, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer–Patient Version
- Pap Test: Can It Detect Ovarian Cancer?
- Persistent Bloating
- Risks and Causes
- Stages and Grades of Ovarian Cancer
- Symptom Diary
- Symptom Diary [+ Video: Recognise the Signs and Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer]
- Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer

- Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer: More Support – Symptoms Diary
- Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer: What Are the Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer?

- Symptoms: Symptom Diary
- Talk With A Doctor If Breast or Ovarian Cancer Runs In Your Family
- Targetovariancancer.org.uk [Target Ovarian Cancer, United Kingdom]
- Tips for Tracking Your Bleeding
- Understanding Gyn Cancers
- Understanding Ovarian Cancer
- Understanding Ovarian Cancer
- Videos and Podcasts: Videos – How Do I Deal With the Menopause After A Diagnosis of Gynaecological Cancer
- What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer? Ovarian Cancer Symptom Diary
- What Are the Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer?
- What Is Ovarian Cancer?
- What Is Ovarian Cancer?
- What Is Ovarian Cancer?
- What Is Ovarian Cancer? [Video]
- World GO Day [World Gynecologic Oncology Day, 20 September]


- World Ovarian Cancer Day May 8, 2025

- Worldovariancancercoalition.org [World Ovarian Cancer Coalition]
- You and Ovarian Cancer: An Animated Patient’s Guide To Ovarian Cancer [+ Animation: Understanding Ovarian Cancer]
Sources
Where may I find the Sources quoted?
You may find the Sources quoted at:
Sources
- Ovarian Cancer Testing & Detection. World Cancer Coalition https://worldovariancancercoalition.org/about-ovarian-cancer/detection-testing/ Accessed: 25 January 2026
- Cancer. National Cancer Institute https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/cancer Accessed: 25 January 2026
- Ovarian Cancer: Ovarian Cancer Basics – What It Is. 12 September 2024. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention https://www.cdc.gov/ovarian-cancer/about/ Accessed: 25 January 2026
- Ovarian Cancer Cancer Symptoms & Risks: What Are the Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer? World Ovarian Cancer Coalition https://worldovariancancercoalition.org/about-ovarian-cancer/symptoms-risk-factors/ovarian-cancer-symptoms/ Accessed: 25 January 2026
- Ovarian Cancer Symptoms & Risks: What Are the Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer? World Ovarian Cancer Coalition https://worldovariancancercoalition.org/about-ovarian-cancer/symptoms-risk-factors/ovarian-cancer-symptoms/ Accessed: 25 January 2026
- Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer: What Are the Symptoms? Last Reviewed: November 2025. Target Ovarian Cancer https://targetovariancancer.org.uk/about-ovarian-cancer/symptoms Accessed: 25 January 2026
- Ovarian Cancer: Main Causes of Ovarian Cancer. Page Last Reviewed: 17 November 2025. NHS https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/ovarian-cancer/causes/ Accessed: 25 January 2026
- Ovarian Cancer Symptoms & Risks: What Are the Risk Factors for Ovarian Cancer? World Ovarian Cancer Coalition https://worldovariancancercoalition.org/about-ovarian-cancer/symptoms-risk-factors/ovarian-cancer-symptoms/ Accessed: 25 January 2026
- Ovarian, Fallopian Tube, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer Screening (PDQ®)–Patient Version: General Information About Ovarian, Fallopian Tube, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer – In the United States, ovarian cancer is the sixth-leading cause of death from cancer in women Updated: 08 May 2025. National Cancer Institute https://www.cancer.gov/types/ovarian/patient/ovarian-screening-pdq#section/_5 Accessed: 25 January 2026
- Ovarian Cancer: How Common It Is. Last Reviewed: 25 November 2024. Cancer Research UK https://about-cancer.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/ovarian-cancer/what-is-ovarian-cancer Accessed: 25 January 2026
- Ovarian Cancer Testing & Detection. World Cancer Coalition https://worldovariancancercoalition.org/about-ovarian-cancer/detection-testing/ Accessed: 25 January 2026
- Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer: What Are the Symptoms? Last Reviewed: November 2025. Target Ovarian Cancer https://targetovariancancer.org.uk/about-ovarian-cancer/symptoms Accessed: 25 January 2026








