“In adults, physical activity contributes to prevention
and management of noncommunicable diseases such as
cardiovascular diseases, cancer and diabetes and…”.1
Umbrella
What may the Physical Activity Health Benefits Umbrella include?
Depending on the Source (DotS) this Umbrella may include:
- Active Living
- Exercise
- Fitness
- Health
- Health Benefits
- Physical Activity
Definition
What is physical activity?
DotS the definition of physical activity may vary. In Physical Activity: Overview the World Health Organization’s (WHO) definition is:
Health Benefits
What is the association between health benefits and physical activity?
In Physical Activity: Key Facts the WHO explain:
- “In adults, physical activity contributes to prevention and management of noncommunicable diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, cancer and diabetes and reduces symptoms of depression and anxiety, enhances brain health, and can improve overall well-being”.3
In Exercise: Benefits of Exercise: Health Benefits the (United Kingdom) NHS elaborate on:
 “People who do regular physical activity have a lower risk of:
“People who do regular physical activity have a lower risk of:
- Coronary heart disease and stroke
- Type 2 diabetes
- Bowel cancer
- Breast cancer in women
- Early death
- Osteoarthritis
- Hip fracture
- Falls (among older adults)
- Depression
- Dementia, including Alzheimer’s Disease
Research also shows that physical activity can boost self-esteem, mood, sleep quality and energy, as well as reducing your risk of stress”.4
In Physical Activity: Benefits of Staying Active the (Australian) Jean Hailes for Women’s Health (JH) explain:
- Reduce your risk of physical health conditions (e.g. heart disease, type 2 diabetes and some cancers)
- Reduce your risk of falls
- Reduce your stress and anxiety
- Improve your sleep
- Improve your concentration
- Make you feel more energetic
- Build social connections”.5
Breast Cancer
Is there an association between breast cancer and physical activity?
In Physical Activity and Cancer: What Is Known About the Relationship Between Physical Activity and Cancer Risk? the (United States) National Cancer Institute elaborate on:
- “Breast cancer: Many studies have shown that physically active women have a lower risk of breast cancer than inactive women. In a 2016 meta-analysis that included 38 cohort studies, the most physically active women had a 12–21% lower risk of breast cancer than those who were least physically active. Physical activity has been associated with similar reductions in risk of breast cancer among both premenopausal and postmenopausal women. Women who increase their physical activity after menopause may also have a lower risk of breast cancer than women who do not”.6
Mood
Is there an association between mood and physical activity?
In Depression: How Can I Take Care of Myself? the (United States) National Institute of Mental Health note:
- “Try to get physical activity. Just 30 minutes a day of walking can boost your mood”.7
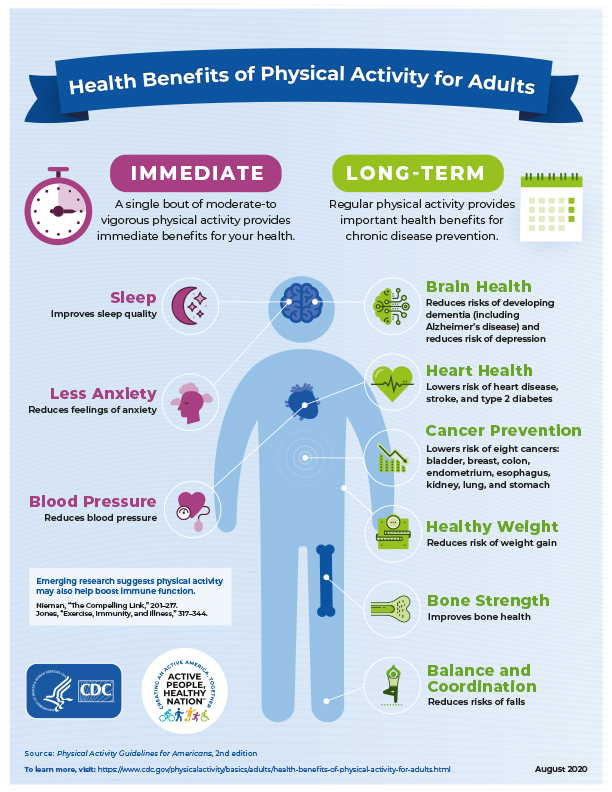
On page 56 in Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, 2nd Edition: Chapter 4. Active Adults – Key Guidelines for Adults the (United States) Department of Health and Human Services explain:
Health Care Provider
What if I am going to start doing physical activity?
If you are going to start doing physical activity, it may be in your best interest to choose to talk to your health care provider about this.
In Physical Activity: Information – Getting Started the (United States) MedlinePlus note:
- You have diabetes, heart disease, lung disease, or another long-term illness
- You have obesity
- You have not been very active lately
- You get chest pains or shortness of breath when you are active”.9
In Fitness: In-Depth – Exercise: 7 Benefits of Regular Physical Activity – The Bottom Line on Exercise the (United States) Mayo Clinic caution:
“Remember to check with a health care professional before starting a new exercise program, especially if you have any concerns about your fitness or haven’t exercised for a long time. Also check with a health care professional if you have chronic health problems, such as heart disease, diabetes or arthritis”.10
Health Topics A-Z
Where may I find Health Topics A-Z related to Physical Activity Health Benefits?
In Health Topics A-Z you may find:
Links
Where may I find Links related to Physical Activity and Health Benefits?
Your Country may have Links similar to:
Links
This Links List to third party websites is neither comprehensive nor exhaustive. Inclusion on this Links List does not imply endorsement or recommendation. Non-inclusion on this Links List does not imply non-endorsement or non-recommendation. Third party websites are not under the control of Meno Martha International Menopause Directory. Third party websites may contain explicit medical images and/or sexual references. Please read Meno Martha International Menopause Directory’s Links Policy before proceeding to a Link. Please contact Webmaster if you experience a problem with a Link.New or Updated
- A Growing Understanding of the Link Between Movement and Health [10 April 2024]
- Mayo Clinic Minute: Aging and the Benefits of Exercising [21 January 2025] [+ Video Courtesy: Mayo Clinic News Network]
- Should You Try the 7-Minute Workout? [+ Video]
- The 30-30-30 Method: How TikTok’s Latest Fitness Trend Could Help You Build Healthy Habits Into Your Day [31 May 2024]
- The Many Benefits of Resistance Training As You Age [27 September 2024]
- Why You Shouldn’t Be Afraid To Start Running After Middle Age [20 April 2024]
- 5 Surprising Benefits of Walking
- 7 Benefits of Regular Physical Activity
- 8 Posture Exercises To Sit and Stand Straighter
- A Growing Understanding of the Link Between Movement and Health
- Be Physically Active
- Can Taking A Plunge In Icy Water After Your Workout Be Beneficial?
- Daily Food and Activity Diary
- Effect of Stress-Related Neural Pathways on the Cardiovascular Benefit of Physical Activity
- Eight Hours of Interval Sprinting Can Reverse Negative Effects of Menopause
- Exercise In Menopause
- Every Move Counts – Launch of the New WHO Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviours
- Exercise
- Exercise Calorie Calculator
- Exercise To Prevent Heart Disease
- Exercise and Immunity
- Exercise and Physical Fitness
- Exercise and Stress: Get Moving To Manage Stress
- Exercise, Lifestyle, and Your Bones
- Exercise: Benefits of Exercise
- Exercise: Benefits of Exercise: What Counts? Keep Healthy With 150 Minutes of Exercise A Week [Video]
- Exercising In Short Bursts May Be As Good for Longevity As Doing It All At Once
- FAQs: Staying Active: Physical Activity and Exercise
- Fitness
- Fitness Basics
- Fitness Studio Exercise Videos
- Fitness and Exercise [Topics]
- Fitness: Basics – Fitness: Basics
- Fitness: In-Depth – Exercise: 7 Benefits of Regular Physical Activity
- Get Active
- Get Happy: Why Exercise Can Lift Your Mood
- Get Moving: Key Takeaways From the New Physical Activity Guidelines
- Get Walking With This 12-Week Walking Schedule
- Get the Facts on Exercise and Chronic Disease
- Getting Active
- Getting Active
- Guide To Physical Activity
- Health Benefits of Cycling and Dos and Don’ts
- Healthy Weight and Growth: Physical Activity and Your Weight and Health
- Heart Health: Movement and Motivation
- How Exercise Can Lead To A Healthy Gut
- How To Measure Your Waist
- In the Loop: Exercise Doesn’t Have To Be “Exercise”
- May Is Osteoporosis Awareness Month

- Mayo Clinic Minute: Aging and the Benefits of Exercising [+ Video]
- Mayo Clinic Minute: Updated Exercise Guidelines for Cancer Patient, Survivors
- Menopause Patient Information [Videos] 5. Lifestyle Advice In Menopause & Perimenopause
- Menopause Preparedness Toolkit Video Series: Lifestyle Tips for Menopause
- Midlife Weight Gain: What’s Really Going On
- Moveyourway [Move Your Way: Walk. Run. Dance. Play. What’s Your Move?]

- Overcoming Midlife Barriers To Exercise and Better Health
- Physical Activity
- Physical Activity
- Physical Activity
- Physical Activity
- Physical Activity
- Physical Activity
- Physical Activity Does More Than Help You Look Good
- Physical Activity and Cancer
- Physical Activity and Your Mental Health
- Physical Activity: Benefits of Staying Active
- Physical Activity: Measuring Physical Activity Intensity
- Physical Activity: Physical Activity Boosts Brain Health
- Physical Activity Basics: Adding Physical Activity As An Adult
- Physical Activity Basics: Adult Activity: An Overview
- Physical Activity Basics: Benefits of Physical Activity
- Physical Activity Basics: Health Benefits of Physical Activity
- Physical Activity Basics: Physical Activity Basics and Your Health
- Physical Activity Basics: Physical Activity and Cancer
- Physical Exercise
- Should You Try the 7-Minute Workout? [+ Video]
- Sleep, Food, Exercise, Stress: Why Working on One of These Can Improve the Others
- The 30-30-30 Method: How TikTok’s Latest Fitness Trend Could Help You Build Healthy Habits Into Your Day
- The Exercise Effect
- The Many Benefits of Resistance Training As You Age
- Tips for Getting More Active Minutes
- Upping Your Step Count, Even In Small Amounts, May Increase Life Span
- Walking
- What Is Slow Running and Does It Work?
- Why Exercise Matters for Your Heart Health
- Why You Shouldn’t Be Afraid To Start Running After Middle Age
Sources
Where may I find the Sources quoted?
You may find the Sources quoted at:
Sources
- Physical Activity: Key Facts. 26 June 2024. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/physical-activity Accessed: 25 March 2025
- Physical Activity: Overview. 26 June 2024. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/physical-activity Accessed: 25 March 2025
- Physical Activity: Key Facts. 26 June 2024. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/physical-activity Accessed: 25 March 2025
- Exercise: Benefits of Exercise: Health Benefits. Page Last Reviewed: 15 August 2024. NHS https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/exercise/exercise-health-benefits/#health-benefits Accessed: 25 March 2025
- Physical Activity: Benefits of Staying Active. Last Updated: 11 May 2024 | Last Revised: 02 February 2024. Jean Hailes for Women’s Health https://www.jeanhailes.org.au/health-a-z/healthy-ageing/physical-activity Accessed: 25 March 2025
- Physical Activity and Cancer: What Is Known About the Relationship Between Physical Activity and Cancer Risk? Reviewed: 10 February 2020. National Cancer Institute https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/obesity/physical-activity-fact-sheet#q2 Accessed: 25 March 2025
- Depression: How Can I Take Care of Myself? Revised: 2024. National Institute of Mental Health https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/publications/depression Accessed: 25 March 2025
- Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans, 2nd Edition: Chapter 4. Active Adults – Key Guidelines for Adults. 2018:56. Department of Health and Human Services https://health.gov/paguidelines/second-edition/pdf/Physical_Activity_Guidelines_2nd_edition.pdf#page=55 Accessed: 25 March 2025
- Physical Activity: Information – Getting Started. Review Date: 27 April 2023. MedlinePlus https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001941.htm Accessed: 25 March 2025
- Fitness: In-Depth – Exercise: 7 Benefits of Regular Physical Activity – The Bottom Line on Exercise. 26 August 2023. Mayo Clinic https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/fitness/in-depth/exercise/art-20048389 Accessed: 25 March 2025








