“Migraine is affected by the changing hormone environment, with perimenopause associated with increased migraine, particularly menstrual migraine”.1
Umbrella
What may the Menopause Headaches Umbrella include?
Depending on the Source (DotS) this Umbrella may include:
- Hormonal Headaches and Migraines
- Menopausal/Menopause Headaches and Migraines
- Perimenopausal/Perimenopause Headaches and Migraines
Headaches
Is there an association between headaches and perimenopause?
In Menopause FAQs: Understanding the Symptoms – Q. I’ve been having headaches lately. Is this a symptom of menopause? the North American Menopause Society (NAMS) elaborate on:
“A. Studies suggest that hormones may play a role in headaches. Women at increased risk for hormonal headaches during perimenopause are those who have already had headaches influenced by hormones, such as those with a history of headaches around their menstrual periods (so-called menstrual migraines) or when taking oral contraceptives. Hormonal headaches typically stop when menopause is reached and hormone levels are consistently low”.2
Migraines
Is there an association between migraines and menopause?
In Migraine: Can Migraine Be Worse During Menopause? the Office on Women’s Health, United States Department of Health and Human Services, Womenshealth.gov elaborate on:
But for some women, menopause worsens migraine or triggers them to start. It is not clear why this happens. Menopausal hormone therapy, which is prescribed for some women during menopause, may be linked to migraines during this time. In general, though, the worsening of migraine symptoms goes away once menopause is complete”.3
Menstrual Migraine
How common is menstrual migraine?
In Menstrual and Perimenopausal Migraine: A Narrative Review – Highlights, dated 09 July 2020, the author notes:
- “During the reproductive years menstrual migraine affects around 4–8% of all women and around 20–25% of women with migraine”.4
Cause
What may cause migraine?
In Menstrual and Perimenopausal Migraine: A Narrative Review – Abstract the author also elaborates on:
Headache Diary
Where may I find a headache diary?
Your Country may have Links similar to:
Treatment
How are headaches treated?
The NAMS explain:
HRT
Can hormone replacement therapy (HRT) help?
On page one in Migraine and HRT: Can HRT Help? the (British) Women’s Health Concern elaborate on:
 “Many women notice that migraine is more likely to occur when they have bad hot flushes and night sweats. Since HRT is very effective at controlling these menopause symptoms, it may help reduce the likelihood of migraine but is not in itself an effective migraine treatment. Further, if started too early in the perimenopause when estrogen levels can fluctuate widely, the addition of HRT can worsen migraine.
“Many women notice that migraine is more likely to occur when they have bad hot flushes and night sweats. Since HRT is very effective at controlling these menopause symptoms, it may help reduce the likelihood of migraine but is not in itself an effective migraine treatment. Further, if started too early in the perimenopause when estrogen levels can fluctuate widely, the addition of HRT can worsen migraine.
The type of HRT is important as some forms of HRT can create more hormone fluctuations, triggering migraine. This is more likely to occur with oral HRT than with patches or gel. We generally recommend that women with migraine who need HRT should use estrogen patches, gel or spray, known as transdermal estrogen, as these provide more stable hormone levels than tablets”.7
Health Care Provider
What if I get headaches?
If you get headaches it may be in your best interest to choose to talk to your health care provider about this. Together you can identify any patterns, discuss your options and if required, agree on who may be the most appropriate health care provider to help you.
The NAMS note:
“If a headache is unusually painful or different from those you have had before, seek medical help promptly”.8
In Headaches: See A GP If the (United Kingdom) NHS also note:
- Your headache keeps coming back
- Painkillers do not help and your headache gets worse
- You have a bad throbbing pain at the front or side of your head – it could be a migraine or, more rarely, a cluster headache
- You feel sick, vomit and find light or noise painful”.9
Who is a GP?
DotS and/or DotC (Depending on the Country) a GP may be a qualified and registered general practitioner, a medical practitioner, a medical doctor or a doctor.
Health Topics A-Z
Where may I find Health Topics A-Z related to Menopause Headaches?
In Health Topics A-Z you may find:
Links
Where may I find Links related to Menopause Headaches?
Your Country may have Links similar to:
Links
This Links List to third party websites is neither comprehensive nor exhaustive. Inclusion on this Links List does not imply endorsement or recommendation. Non-inclusion on this Links List does not imply non-endorsement or non-recommendation. Third party websites are not under the control of Meno Martha International Menopause Directory. Third party websites may contain explicit medical images and/or sexual references. Please read Meno Martha International Menopause Directory’s Links Policy before proceeding to a Link. Please contact Webmaster if you experience a problem with a Link.New or Updated
- Does Caffeine Help Migraines?
- Mayo Clinic Q&A: Managing Migraine: What’s Right for Me? [02 May 2024]
- Menopause and Migraines: New Findings Point To Power of Prevention [14 February 2024]
- Menopause, Perimenopause and Migraine [28 February 2024]
- Video Series-2024: Preparing for Your Menopause Health Care Visit [13 January 2024]
- Webinars: Previous – Brain Teasers: Challenges In the Cranium
- 10 Common Migraine Triggers and How To Cope With Them
- 6 Tips for Headache Relief
- Are Migraines Hereditary?
- BMS TV: Headaches, Migraines and the Menopause
- Does Caffeine Help Migraines?
- Factsheets and Resources
- Find A Menopause Practitioner [United States and Other]
- Find An AMS Doctor [Australasian Menopause Society i.e. Australia and New Zealand]
- Find Your Nearest BMS Menopause Specialist [British Menopause Society]
- Headache
- Headache Diaries & Migraine Diaries
- Headache Diary: Keeping A Diary Can Help Your Doctor Help You [+ Format]
- Headache Topic Sheet
 Headache Types [A-Z]
Headache Types [A-Z]- Headache – Multiply Languages
- Headaches and Hormones: What’s the Connection? During Perimenopause and Menopause
- Headaches.org [National Headache Foundation, United States]: Resources
- Headaches
- Headaches: Reduce Stress To Prevent the Pain
- Headaches: Overview – What Are the Types of Headache? Primary Headaches
- Heads Up: What Your Headache Location Means
- Here’s Why You’re Always Waking Up With Headaches
- How Can Mindfulness Practices Help With Migraine?
- How To Quit Caffeine Without A Headache
- June Is Migraine & Headache Awareness Month! [United States]
- Keeping A Headache Diary
- Later Years (Around 50 Years and Over): Menopause and Post Menopause Health – Signs and Symptoms of Menopause [+ Video: Talking Menopause With Your GP] [Other Languages and Formats]
- Later Years (Around 50 Years and Over): Menopause and Post Menopause Health – Supporting Someone Through the Menopause [+ Video: Men Don’t Need To Know About Menopause] [Other Languages and Formats]
- Living Mentally Well With Chronic Pain Conditions
- Managing Migraines At Home
- Managing Tension Headaches At Home
- Mayo Clinic Expert Offers Tips To Prevent, Manage Headaches, From Migraine To ‘Rebound’
- Mayo Clinic Minute: Better-Tolerated Treatments for Migraine Pain [+ Video Courtesy: Mayo Clinic News Network]
- Mayo Clinic Minute: It’s the Season for Cluster Headaches [+ Video Courtesy: Mayo Clinic News Network]
- Mayo Clinic Minute: Managing Migraines In the Summer [+ Video]
- Mayo Clinic Q and A: Botox for Migraines
- Mayo Clinic Q and A: Perimenopause Transitions and Concerns
- Mayo Clinic Q&A: Managing Migraine: What’s Right for Me?
- Menopause
- Menopause FAQs: Menopause Symptoms – Q. I’ve Been Having Headaches Lately. Is This A Symptom of Menopause?
- Menopause Map: Downloadable Resources – My Personal Path Print Tools: Questions for Your Health Care Provider

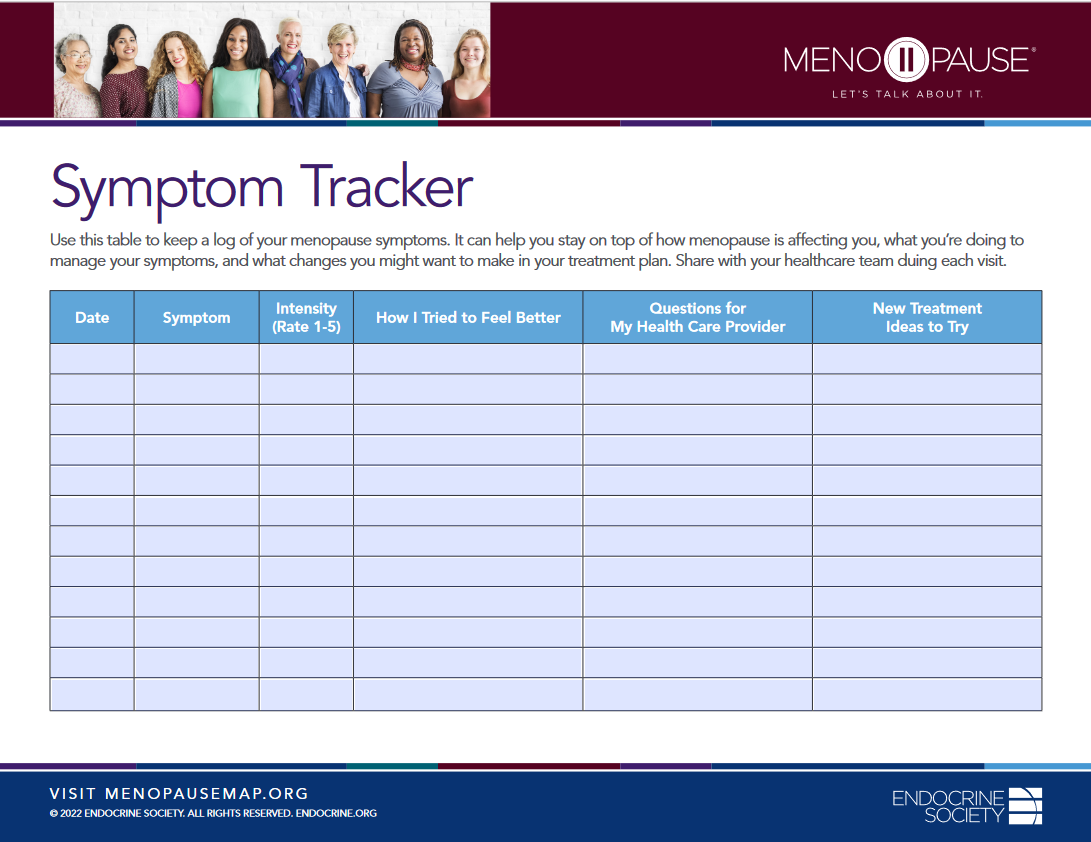
- Menopause Map: Downloadable Resources – My Personal Path Print Tools: Symptom Tracker
- Menopause Patient Information [Videos] 5. Lifestyle Advice In Menopause & Perimenopause
- Menopause Preparedness Toolkit Video Series: Common Conditions Associated With Menopause and Midlife
- Menopause Preparedness Toolkit Video Series: Lifestyle Tips for Menopause
- Menopause Preparedness Toolkit Video Series: Mindfulness & Wellbeing During the Menopause Transition
- Menopause Preparedness Toolkit: A Woman’s Empowerment Guide
- Menopause and Migraine
- Menopause and Migraines: New Findings Point To Power of Prevention
- Menopause, Perimenopause and Migraine
- Menopause: Understanding the Changes and Finding Relief | Dr Susan Davis | The Proof Podcast EP 256
- Menstrual Migraine
- Menstrual Migraines (Hormone Headaches)
- Migraine
- Migraine
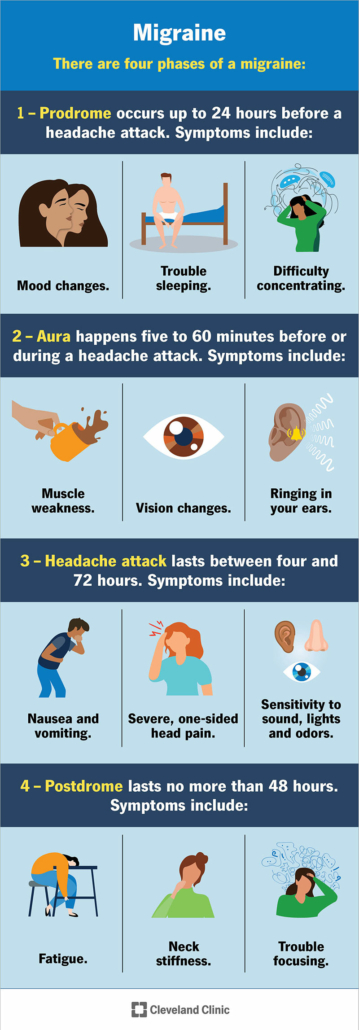 Migraine
Migraine- Migraine Headaches
- Migraine In Women
- Migraine Patient Toolkit: A Guide To Your Care
- Migraine Patient Toolkit: Living Well With Migraine
- Migraine Triggers
- Migraine and Food
- Migraine and HRT
- Migraine and Headache Diary
- Migraine and Hormones
- Migraine and Menopause
- Migraine and Menopause Webinar Recap [+ Video]
- Migraine and Menopause – A Narrative Review [+ Video Summary]
- Migraine and Perimenopause
- Migraines and Menopause
- Migraines: Simple Steps To Head off the Pain
- National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health: Headaches – What You Need To Know
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke: Headache Information Page
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke: Migraine Information Page
- Nationalmigrainecentre.org.uk
- Navigating Menopause: Expert Insights and Solutions | Dr Susan Davis | The Proof Podcast EP 245
- Perimenopause
- Perimenopause
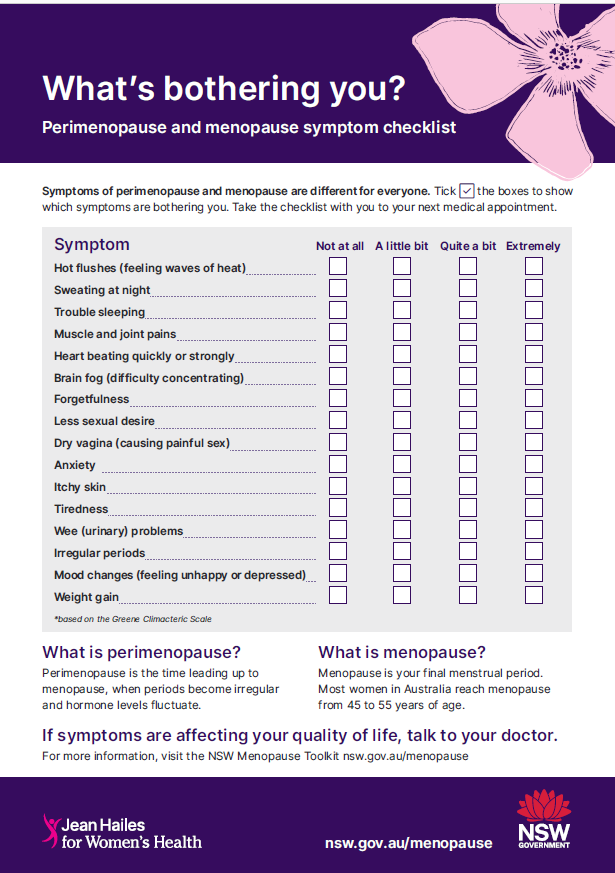
- Perimenopause and Menopause Symptom Checklist
- Reducing Migraines Through Lifestyle Modifications
- Science Saturday: Opioids Provide Low Evidence of Pain Relief for Migraine
- Struggling With Migraine Hangovers? Read This
- Tension Headache
- Tension-Type Headaches: Self-Care Measures for Relief
- The Truth About Menopause Supplements | Dr Sarah Berry
- Tips To Help Manage Menopause Symptoms
- Tools for Living With Migraine and Headache Disorders
- Top 30 Things I Wish I Knew…. [+ Videos]
- Using Natural Therapies In the Menopause Transition – Webinar
- Video Series-2023: NAMS 2023 Nonhormone Therapies Position Statement for Bothersome Menopause Symptoms
- Video Series-2023: New FDA-Approved Nonhormone Option for the Treatment of Hot Flashes
- Video Series-2024: Preparing for Your Menopause Health Care Visit
- Videos and Podcasts: Videos – Interviews: Migraine Headaches
- Webinars: Previous – Brain Teasers: Challenges In the Cranium
- What Is Migraine?
- When Headaches Won’t Go Away
- When Migraine Turns Chronic
- Why Am I Waking Up With A Migraine?
- Women and Migraines: What You Need To Know
Sources
Where may I find the Sources quoted?
You may find the Sources quoted at:
Sources
- MacGregor, E. A. Menstrual and Perimenopausal Migraine A Narrative Review – Abstract. 09 July 2020. https://www.maturitas.org/article/S0378-5122(20)30329-7/pdf Accessed: 08 March 2024
- Menopause FAQs: Menopause Symptoms – Q. I’ve been having headaches lately. Is this a symptom of menopause? North American Menopause Society https://www.menopause.org/for-women/menopause-faqs-menopause-symptoms Accessed: 08 March 2024
- Migraine: Can Migraine Be Worse During Menopause? Page Last Updated: 22 February 2021. Office on Women’s Health, United States Department of Health and Human Services, Womenshealth.gov https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/migraine Accessed: 08 March 2024
- MacGregor, E. A. Menstrual and Perimenopausal Migraine A Narrative Review – Highlights. 09 July 2020 https://www.maturitas.org/article/S0378-5122(20)30329-7/pdf Accessed: 08 March 2024
- MacGregor, E. A. Menstrual and Perimenopausal Migraine A Narrative Review – Abstract. 09 July 2020 https://www.maturitas.org/article/S0378-5122(20)30329-7/pdf Accessed: 08 March 2024
- Menopause FAQs: Menopause Symptoms – Q. I’ve been having headaches lately. Is this a symptom of menopause? North American Menopause Society https://www.menopause.org/for-women/menopause-faqs-menopause-symptoms Accessed: 08 March 2024
- Migraine and HRT: Can HRT Help? Reviewed: November 2023:1. Women’s Health Concern https://www.womens-health-concern.org/help-and-advice/factsheets/migraine-and-hrt/ Accessed: 08 March 2024
- Menopause FAQs: Menopause Symptoms – Q. I’ve been having headaches lately. Is this a symptom of menopause? North American Menopause Society https://www.menopause.org/for-women/menopause-faqs-menopause-symptoms Accessed: 08 March 2024
- Headaches: See A GP If. Page Last Reviewed: 09 February 2021. NHS https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/headaches/#when-to-get-medical-help Accessed: 08 March 2024



